ByteDance’s Culture Clash: How TikTok’s Parent Company Is Coping with its Internal Struggle
As TikTok faces mounting global scrutiny, another storm is brewing inside its parent company ByteDance - one that could influence the fate of the world’s most valuable startup. Exclusive employee sentiment data reveals a company divided, where culture clashes and compliance risks threaten to derail its global ambitions.
ByteDance is one of the most powerful tech companies in the world, but its rapid global expansion has exposed deep internal tensions. As its flagship app, TikTok, continues to face regulatory scrutiny in the U.S. and beyond amid concerns over data privacy, content moderation, and national security, the company’s internal culture tells a similarly fraught story.
Aniline’s employee sentiment data offers a unique window into the organizational challenges at ByteDance. These insights reveal stark differences in how employees experience the workplace depending on their location. While TikTok dominates headlines, internal struggles with leadership, compliance, and workplace culture clashes are quietly shaping the future of the company itself.
Employees outside of China describe a workplace dominated by Chinese management practices, creating friction in leadership style, communication, and career advancement. Compliance issues also loom large, as ByteDance takes a China-first approach to governance, often clashing with local labor laws and regulatory expectations. Many of the same concerns that fuel TikTok’s regulatory battles - questions of oversight, transparency, and governance - also impact ByteDance’s global workforce, particularly in Western markets.
At the heart of these issues is a deep cultural divide. Non-Chinese employees report feeling excluded from key decision-making, facing barriers to promotion, and struggling with a lack of transparency in HR policies. Diversity, equity, and inclusion efforts appear inconsistent, with employees in Western offices expressing concerns about favoritism toward Chinese staff. These challenges raise a critical question: can ByteDance truly succeed as a global company while holding onto its China-centric approach?
What do ByteDance employees really think about working for the tech giant, about how compliance gaps and governance blind spots can pose long-term risks, and about whether the company can successfully bridge the gap between its Chinese leadership and its increasingly global workforce?
Employee Experiences: China vs. Global Offices
While ByteDance operates in numerous countries, employee experiences vary drastically based on location. Chinese employees tend to describe a highly structured, fast-moving workplace, with strong collaboration and a deep alignment with company values. However, employees outside of China report a different reality, where the company’s rigid structure and preference for Chinese leadership create challenges in career advancement, decision-making, and day-to-day operations.
One of the biggest sources of frustration among non-Chinese employees is the language barrier, with observations such as “a lot of internal documentation is in Chinese, making it difficult to fully understand policies and processes.” Meetings often default to Mandarin, even in global offices, creating an environment where non-Chinese employees struggle to keep up with critical company decisions. These barriers contribute to what some describe as a “second-tier” status for non-Chinese employees, limiting their access to leadership roles and key projects.
Time zone challenges also add to the frustration. With ByteDance’s headquarters in Beijing, employees in Western offices frequently report late-night or early-morning meetings to accommodate Chinese leadership’s schedules. “You’re expected to be available around the clock,” an employee noted. These expectations, combined with high turnover rates, create an exhausting work environment that many say is unsustainable.

Culture Clash: Leadership Style & Workplace Exclusion
While financial metrics offer one lens into Walgreens' challenges, our comprehensive analysis revealed that the company's most pressing issues were fundamentally human. Employee feedback painted a concerning picture of an organization where frontline workers felt increasingly disconnected, unsupported, and unable to deliver the service they aspired to provide.
The transaction documents indicate that Sycamore and Walgreens leadership understand the need to address these fundamental human capital issues. The strategic vision emphasizes "enhancing the customer, patient and team member experience with continued investments in the core pharmacy operations."
The Roadmap to Success for New Ownership
The tension between ByteDance’s Chinese leadership style and the expectations of a global workforce is one of the most significant issues employees highlight. The company’s leadership model prioritizes hierarchy, speed, and strict adherence to directives—an approach that often clashes with Western norms of autonomy, collaboration, and transparency.
Many employees outside of China feel disconnected from leadership, describing a work culture where decisions are made behind closed doors, often without input from regional teams, with statements like “there’s little room for questioning or feedback—it’s top-down management, and that’s final.” This style, while effective in ByteDance’s home market, has caused friction in regions where employees expect more involvement in shaping company strategy.

This leadership disconnect also fuels concerns about bias in promotions and performance reviews, with advancement opportunities being perceived as mostly reserved for Chinese employees, with employee comments like "no matter how high you grow, a Chinese [person] will ultimately be your boss." This sentiment is reinforced by reports of non-Chinese employees being overlooked for leadership positions in favor of colleagues who are seen as more aligned with the company’s internal norms. The result is a growing divide between ByteDance’s global workforce and the leadership structure at its core.
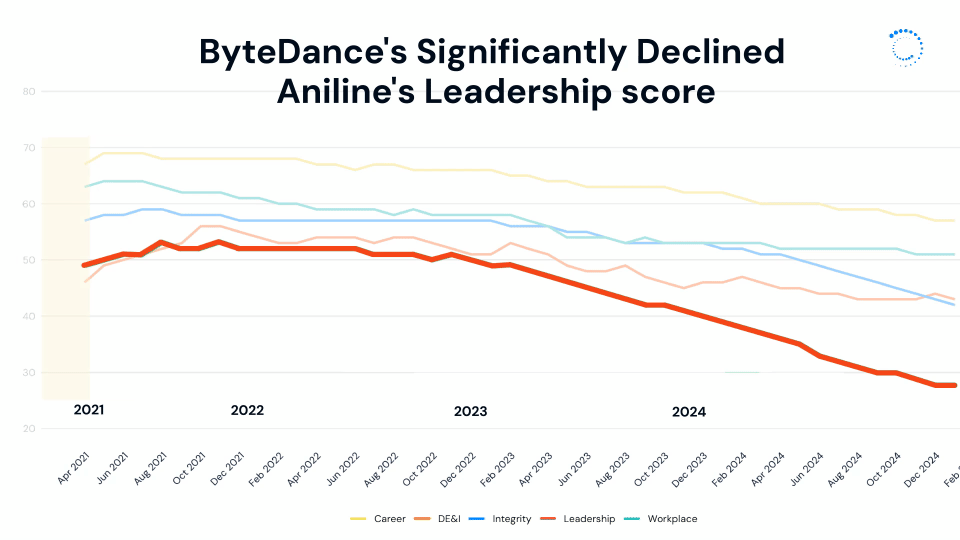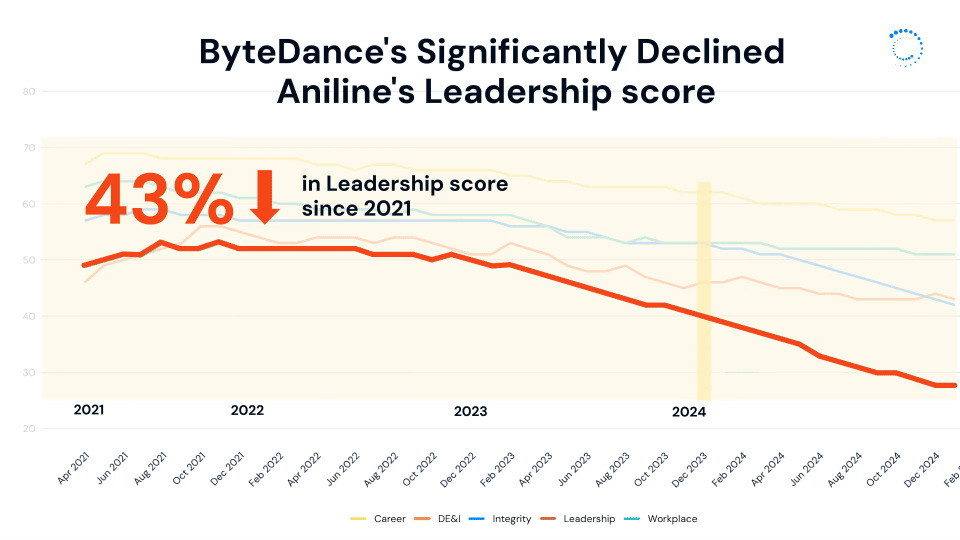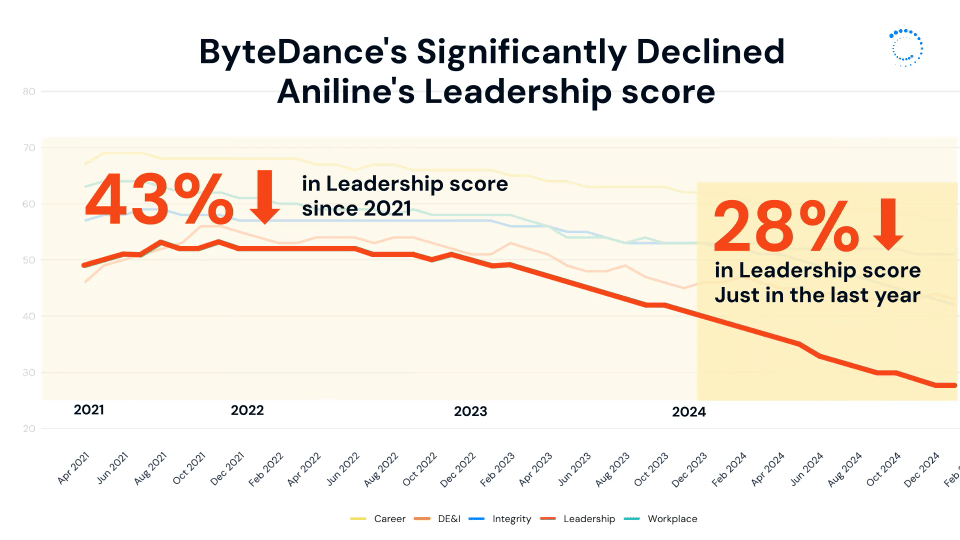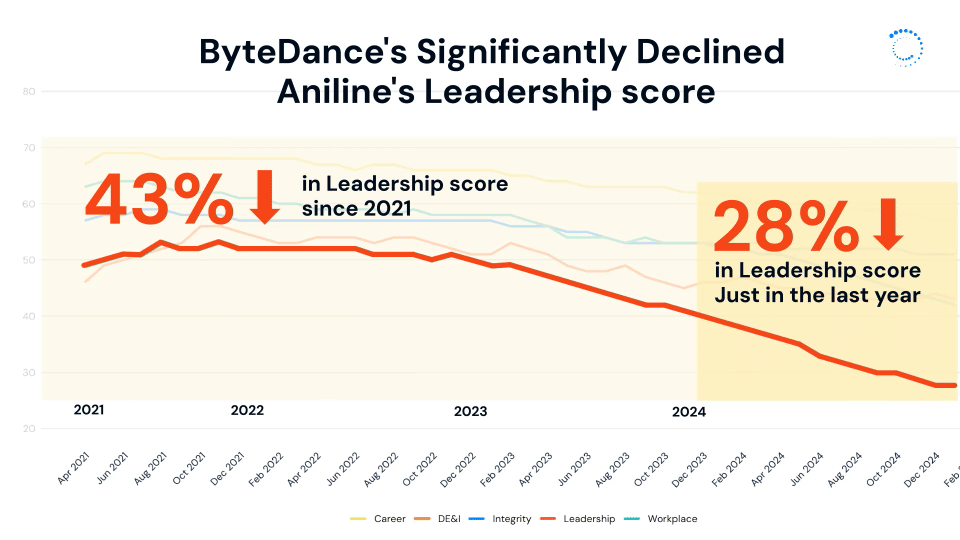
This divide is perhaps part of the reason ByteDance’s leadership score has declined so significantly over time, dropping 28% in the last year alone and over 40% since 2021.
This leadership disconnect also fuels concerns about bias in promotions and performance reviews, with advancement opportunities being perceived as mostly reserved for Chinese employees, with employee comments like "no matter how high you grow, a Chinese [person] will ultimately be your boss." This sentiment is reinforced by reports of non-Chinese employees being overlooked for leadership positions in favor of colleagues who are seen as more aligned with the company’s internal norms. The result is a growing divide between ByteDance’s global workforce and the leadership structure at its core.
This divide is perhaps part of the reason ByteDance’s leadership score has declined so significantly over time, dropping 28% in the last year alone and over 40% since 2021.
Compliance Gaps & Governance Risks
ByteDance’s China-first approach doesn’t just create internal friction—it also raises serious compliance and regulatory concerns. The company’s global expansion has often been accompanied by a lax approach to local labor laws, workplace policies, and ethical business practices. Employees have expressed concerns about inconsistent HR enforcement, lack of transparency in dispute resolution, and unclear policies around data privacy.“There’s no real effort to adapt to local regulations,” one employee noted. “The expectation is that the Chinese way of doing business applies everywhere.” This approach has led to clashes with labor regulators in various countries, with employees in Western offices citing issues like unpaid overtime, arbitrary contract changes, and a lack of clear workplace protections.
Data privacy is another area where ByteDance faces scrutiny, both externally and internally. While regulators question how TikTok handles user data, employees report similar concerns about internal data security practices. “There’s a lack of clarity around how employee and customer data is handled—things happen behind the scenes with little oversight,” one employee stated. As governments impose stricter regulations on data governance, ByteDance’s reluctance to adapt to local compliance standards could pose long-term risks.
Can ByteDance Bridge the Divide?
ByteDance’s meteoric rise has been fueled by innovation, but its ability to sustain global success depends on more than just cutting-edge technology. Employee sentiment, as captured by Aniline’s data, suggests that the company’s China-centric approach is creating deep challenges in leadership, workplace culture, and compliance. The company has already set aside $1 billion to cover future European Union penalties related to investigations into TikTok, and the TikTok ban in the U.S. is estimated to equate to $1 billion in monthly revenue losses. How many more similar costs will ByteDance incur through repeated refusals to adapt to global norms and operating standards?
For ByteDance to thrive as a truly global enterprise, it must address the growing cultural divide within its workforce. This means fostering greater transparency in leadership, adapting workplace policies to local markets, and ensuring that non-Chinese employees have equal opportunities for growth. As regulators and employees alike continue to scrutinize its practices, the company’s willingness to evolve will determine whether it can remain a dominant force in the tech industry, or whether internal fractures will weaken its global ambitions.
.png?width=4334&height=1355&name=Logo%20with%20name_Blue%2BYellow%20(1).png)